mySoftware [Updates]
newProducts [YOK]
Moving a MOX6/MOX8 SONG into a Cubase Project
QUESTION: I’d like to bring my Song’s MIDI tracks into Cubase on individual MIDI tracks
GOAL: To be able to add additional tracks and edit in Cubase, create a mix, and begin the process of ‘printing’ the MOX6/MOX8 PARTS as audio tracks.
Moving your MOX6/MOX8 SONG’s MIDI data to Cubase is the first step. You want to work with a “SONG” rather than a PATTERN… you want to take your PATTERNS, Chain them, then convert them to a linear SONG. Reason: because Cubase is also linear in nature. As is always recommended, [STORE] and then SAVE your data as a MOX6/MOX8 ALL data file to a USB drive (.X4A).
What we want to move is the MIDI event data. That is, the MIDI events that are documentented (recorded) in the tracks of the MOX6/MOX8 sequencer, to Cubase MIDI Tracks. The MIDI tracks will be assigned to play from Cubase and trigger the MOX6/MOX8. We will use a file format developed specifically for moving MIDI sequence data universally - the Standard MIDI File
In a separate operation the MIXING data will be moved to the MOX6/MOX8 Editor VST, which conveniently runs inside of Cubase. While MIDI event data is fairly standard, the MOX6/MOX8 mix and Voice parameters are specifcally YAMAHA parameters and therefore are moved in a separate proprietary format. The MIXING parameters are those concerning the MOX tone engine (synthesizer) - and are therefore not the kind of data that is in the MIDI Tracks. The VOICES you selected for each PART, the pan position, the mix volume, the Reverb send amounts, the Chorus sends, etc., etc., etc. The MIXING setup will still be in your MOX6/MOX8, but what you want to do, is capture this data with the Editor which saves it together in the Cubase Project (very cool). When you recall the Project all your MOX6/MOX8 sounds and mix setup come with it. So you don’t have to keep a version of this in your MOX6/MOX8. *Everything* to make it play correctly will be included in the Cubase Project file (.CPR).
So there are two important steps in this transfer:
_ The MIDI sequencer data.
_ The MIXING tone generator setup (synthesizer data).
CHECKLIST: What you will need for this:
MOX6/MOX8 connected to your computer via USB
The Yamaha Steinberg USB Driver v1.7.2 for Mac/ v1.7.3 for Windows (or later) for your particular computer’s OS
The MOX6/MOX8 Remote Tools v1.1.3 (or later)
The MOX6/MOX8 Editor Standalone VST v1.6.0 (or later)
The audio outputs of the MOX6/MOX8 connected to a quality stereo sound system
http://download.yamaha.com
A named MOX6/MOX8 SONG
Recommended you STORE and then go to FILE and SAVE an ALL data file as a backup (.X4A).
For this example we will set the MOX6/MOX8 to dual stereo record:
(This mode allows you to address the external DAW via two discreet stereo feeds - you route signals as you require to accomplish various recording schemes).
Press [UTILITY]
Press [F5] USB I/O
Press [SF1] OUT CH (OUTPUT CHANNEL Mode)
Verify that the parameter is set to “4CH”

If not, you will need to change it, press [ENTER] and then reboot the MOX6/MOX8 - for the change to take place.
By making 4 Channels available you will be able to address the DAW on two separate Stereo feed - it is all about flexibility and being able to isolate parts when you want to separate them from the rest.
Important note about the [SF1] OUT CH (OUTPUT CHANNEL): Pressing this button calls up the display which determines whether the maximum number of output channels for USB is 4 channels (2 stereo channels) or 2 channels (1 stereo channel). If transfer of the audio signal between the MOX6/MOX8 and the computer connected to the MOX6/MOX8 is compromised or impossible, set this parameter to “2ch.†This setting reduces the CPU load of the computer, and may resolve the problem. After changing this setting, press the [ENTER] button, then restart the MOX6/MOX8.
_ After changing this setting and pressing the [ENTER] button, make sure to restart the MOX6/MOX8; the instrument will not operate otherwise. Before restarting, make sure to store any important edited data to prevent it from being inadvertently lost.
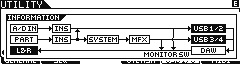
Press [SF6] INFO to view the routing (signal flow) Press [F5] USB I/O
Set MODE = 2StereoRec (Dual Stereo Record Outputs)
Transferring the MIDI data from MOX6/MOX8 to Cubase
1) Save the data as a SMF to a USB stick. Drag and drop the .MID file in an empty Cubase Project and it you can assign it to play from the MOX6/MOX8
2) Transfer the sequence from the MOX6/MOX8 in real time. Synchronize the MIDI clocks (Cubase as master, MOX as slave), open a MIDI Track and run it through once. (This method will be described in a separate article).
In both cases, once the data is recorded to a Cubase MIDI Track you can have it split out to separate Tracks by MIDI channel (using the DISSOLVE PARTS function).
SAVE MOX SONG as a SMF
Connect a USB stick to the USB “To Device” port on the back of the MOX6/MOX8
Press [FILE]
Press [SF2] SAVE
Setup TYPE = SMF
Move the cursor down between the brackets and give your file a Name.
Press [SF1] EXEC
You can now select the SONG that you want to transfer by number/name
Press [SF1] EXEC
This will create a file with the extension .MID
Preparing to Drop the file into Cubase
In Cubase you can setup so that your MIDI file will be quick and easy to assign all the tracks to MOX6/MOX8
Go to your Cubase “Preferences...” > MIDI > MIDI FILE > you want to set the IMPORT OPTIONS:
Check: “Import dropped File as single Part”
Clear all the others options.
Click APPLY
Click OK

When this is activated and you drag and drop a MIDI file into the project, the whole file will be placed on a single track. This is exactly what we want. But before we actually do that you can setup the MOX6/MOX8 as VST within Cubase.
Place the USB stick in your computer.
Launch Cubase
Because you have properly installed the REMOTE TOOLS (which includes the EXTENSIONS) Cubase will ask you if you want to use the Yamaha MOX6/MOX8 as your ASIO interface.
Yes, you do!
Open a NEW PROJECT > use the EMPTY template
Create a NEW FOLDER on your computer (not on the USB stick) to house your Project as directed by Cubase
And again because you have properly installed the REMOTE TOOLS/Extensions, Cubase will automatically setup MIDI, REMOTE, and VST AUDIO SYSTEM settings for you. If not please see the “Cubase: DEVICES Troubleshooting” article.
Go to DEVICES > VST INSTRUMENTS > Click in the first empty item on the instrument rack > EXTERNAL > MOX6/MOX8 VST

You will be asked if you want to create a MIDI Track assigned to this VST device… Create it.
By creating a track assigned to the MOX6/MOX8 VST, this prevent us from having to individually assign each track (manually).
Set the MIDI CH = ANY (literally “ANY")
You can now drag ‘n’ drop the .MID file in the empty track data area, at Measure 1.

You can use the MIDI > DISSOLVE PART function to split the MIDI data out to separate tracks, by MIDI Channel, if you wish (you only need to if you need to edit it, some prefer it, some don’t). If when you click on MIDI, the DISSOLVE PART function is “greyed out” - you must highlight (select) the track data area in Track view window. Set the dialog box that opens to separate the data by MIDI channel.
Now, let’s make sure that Cubase is aware of the MOX6/MOX8 synthesizer data (We are going to import the current MIXING setup and Voice Library)
The MOX6/MOX8 Editor VST and the tone generator settings
Verify your setting within the Editor VST. If you have setup up before it should just come online. However, for the purposes of this article, we will go through the verification steps - so if you ever need to troubleshoot it you will know how to do so:
On the EDITOR VST:
Go to FILE > SETUP
Verify that the USB Port Details are setup as follows:

Notice that the MOX6/MOX8 communicates on two separate PORTS (Port 1 and Port 4). Port 1 is the normal MIDI OUTmessages of musical note, controller and tempo data. Port 4 is used exclusively for bi-directional communication between the Editor and the MOX6/MOX8 hardware (which is external to the computer).
Go to FILE > VSTI SETUP
Verify that your USB AUDIO BUS outputs are setup as follows:

You can bring the synthesizer parameters over to Editor VST by requesting a BULK > DATA SYNC via the Editor VST.
The Editor can pull the data over for you.
In the EDITOR, click on BULK on the main menu and select DATA SYNC
Click on RECEIVE

“Receive” is the computer application receiving data from the MOX6/MOX8 hardware.
Click on the options you want to capture. You can capture the CURRENT (the current Mix settings in your MOX6/MOX8) - so recall the SONG in the MOX and then click OK to capture it.
You can additionally capture all the USER bank VOICES, Drum Kits, and even your marked Favorites! This can be very useful in archiving your data on your computer. You can have every VOICE and every possible thing that you could have used in this Project in one nice neat file.
Once the data is captured and you SAVE the PROJECT - every setting is saved.
You are now able to work with Cubase: Edit the tracks, add additional tracks, mix, begin to bounce your MOX6/MOX8 parts to Cubase (that is print them as Audio Track to Cubase), and go on to complete and even Master your work in a program like WaveLab7.
From this point you can begin to use Cubase to enhance your composition. We should mention that you are now setup to play MIDI data from Cubase > it travels via USB-MIDI to the MOX6/MOX8 hardware which interprets the MIDI messages and generators audio > the audio is routed back to computer via one of two pair of audio buses USB 1/2 and USB 3/4 > the Editor VST is responsible for returning the audio into Cubase such that it behaves like any internal soft synth. This means the virtual audio is going to found in the VST INSTRUMENT Folder. In this VST INSTRUMENT folder you will see “audio lanes”. It is here that you will see meters for USB 1/2 and USB 3/4.
You need to know how to activate the MOX6/MOX8 VST audio return into Cubase.
Go to DEVICES > VST INSTRUMENTS
On this Instrument Rack you will see several icons - the one to the right of the “e” (edit) is the symbol for OUTPUT “[->“ (an arrow pointing to the right). If you click here you can see each pair of audio RETURNS from the MOX6/MOX8 hardware. This is where you can activate and deactivate the second pair.
This should get you started. There is no one way to proceed. In the next article we will deal with the monitoring options available and how to get the most out of this powerful combination.
Permalink

